Free DNA Fetal Kit RhD-Duplex enables early, accurate, and safe determination of the fetal RhD genotype through a non-invasive analysis based on circulating cell-free fetal DNA (cffDNA) in maternal blood. This test is specifically designed for pregnancies of RhD-negative women, with the aim to optimize anti-D immunoglobulin prophylaxis, avoiding unnecessary treatments and reducing healthcare costs.
The test is exclusively intended for the determination of the fetal RhD genotype and it is not indicated for other prenatal determinations such as fetal sex. It is recommended for use in pregnancies of RhD-negative women, who represent approximately 10-15% in Caucasian populations. In Spain, it is estimated that there are approximately 65,000 RhD-negative pregnancies per year and around 13,000 in Portugal. In LATAM, the figures vary significantly by country, ranging from about 8,000 cases in Uruguay to over 500,000 in Brazil.
The analysis is performed from a maternal blood sample collected from the 11th week of amenorrhea. Fetal DNA is extracted from the plasma and analyzed to detect the presence of exons 5, 7, and 10 of the RHD gene by Real Time PCR. Targeting these three exons is essential to ensure 100% analytical sensitivity. The absence or presence of these exons determines whether the fetus is RhD-positive or RhD-negative.
This kit is an exclusive innovation of the Institut de Biotechnologies Jacques Boy (IBJB), and it is the first fetal RhD genotyping test with CE marking Class D under Regulation (EU) 2017/746 for in vitro diagnostic medical devices (IVDR), thus complying with the highest European regulatory standards.
The complete workflow, from plasma DNA extraction to specific amplification of targeted exons, has been validated on automated platforms commonly used in clinical laboratories, facilitating integration and ensuring result reproducibility.
This test is routinely prescribed in different countries to:
– Avoid unnecessary injections of anti-D immunoglobulin in RhD-negative fetuses.
– Focus prophylaxis on pregnancies with true RhD maternal-fetal incompatibility
Key Features
- Non-invasive diagnosis from maternal blood.
- Detection of fetal RhD genotype from the 11th week of gestation.
- High analytical sensitivity: detection of exons 5, 7, and 10 of the RHD gene by RT-PCR.
- CE marked Class D under IVDR (EU) 2017/746.
- Compatible with clinical automated platforms.
- Enables personalized care for pregnant women and minimize the anxiety associated with this condition.
- Reduces unnecessary use of anti-D immunoglobulin.
- Optimizes healthcare resources and lowers associated costs.
Presentation Details
- Kit contents: molecular biology reagents sufficient for 96 reactions, divided into 1 to 6 runs.
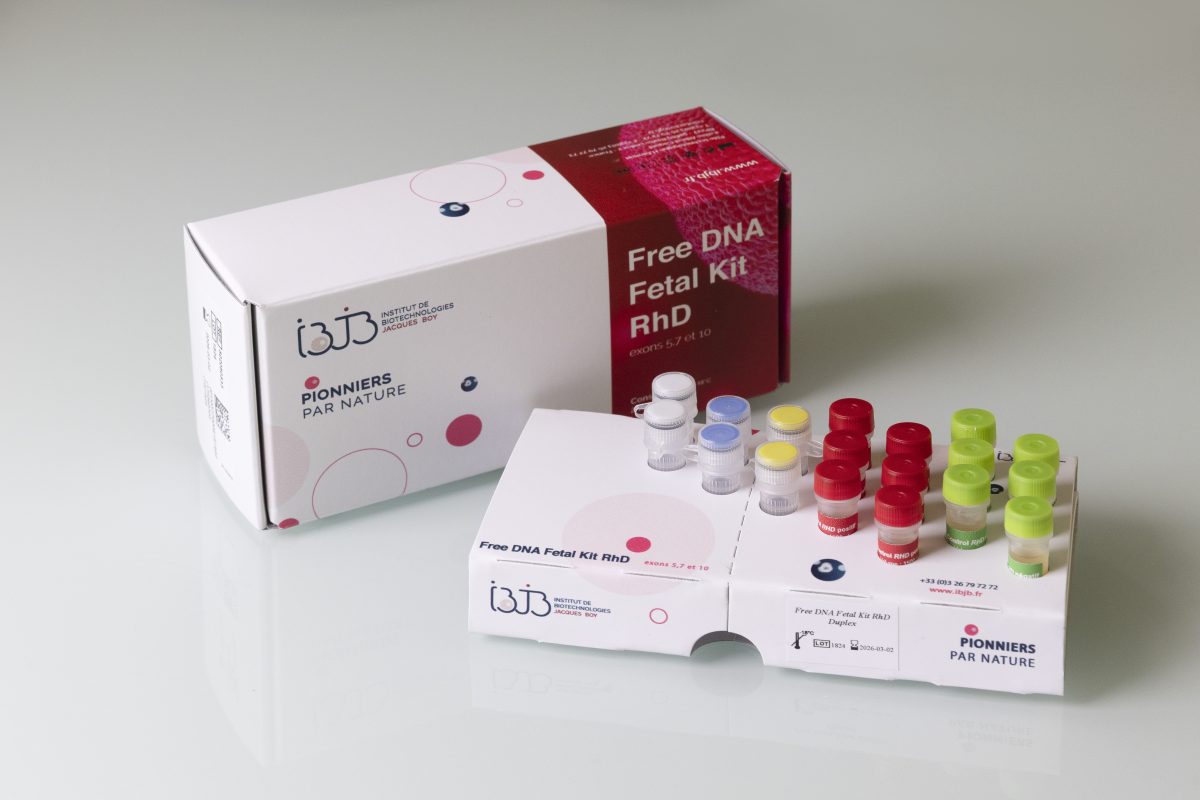
- Exclusive use: RhD fetal genotyping (does not include other prenatal determinations).
- Product code: IBJ 502080533.
- Manufacturer: Institut de Biotechnologies Jacques Boy (IBJB) – Reims, France.